
What Are Wisdom Teeth?
Wisdom teeth or third molars* are a set of 4 teeth, far back in a human's mouth. Many people get them later in their adolescent years or their early 20s. Many people have surgery to get rid of wisdom teeth because they usually grow twisted. Two wisdom teeth on the top and two wisdom teeth on the bottom would be a complete set of 32 adult teeth.
*Molar teeth are big, flat teeth at the back of the mouth.
Why Wisdom Teeth Called Wisdom Teeth?
All of you must have heard from your elders, mainly in your childhood, that wisdom teeth grow out, and when it comes out, it hurts a lot.
Even then, the only question in our minds was whether the intellect comes to man after the wisdom teeth have come out. And does intelligence have anything to do with wisdom teeth?
The third molar has been known as the wisdom tooth since the 17th century, and now in the 21st century, people still use the word wisdom tooth.
The wisdom teeth usually come out later than all our teeth, typically between the ages of 17 and 25.
Molar teeth are called wisdom teeth because they come out when a person becomes an adult, and in this part of his life, he has more intellect and awareness than before. That is why the third molar is commonly called wisdom teeth.
Signs And Symptoms Of Wisdom Teeth
Pain behind the molars at the back of the mouth. This pain will slowly evolve with time as the wisdom teeth continue to develop sideways, or misaligned, touching on bone and nerves and pressing surrounding teeth.
Wisdom teeth signs and symptoms involve pain, tenderness, redness, or swelling. When wisdom teeth come in through the surface of the gums, this permits bacteria to enter into open tissue, which can cause infection. Oral infections can affect your overall health, too.
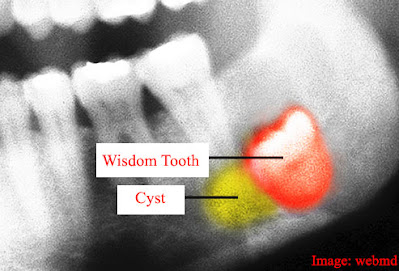
Wisdom teeth can be impacted. The jaw bone or nearby teeth block the teeth from erupting. They can be stuck in place as their roots continue to extend, and if they remain impacted, they cause difficulties for your general health. Wisdom teeth indications because of impaction involve severe pain at the back of the mouth, infection, and other complexities. Bad taste upon chewing, nasty breath, redness, and swelling can all be signs of infection. If not preserved, impacted wisdom teeth can cause blister cysts and, in exceptional circumstances, tumors.
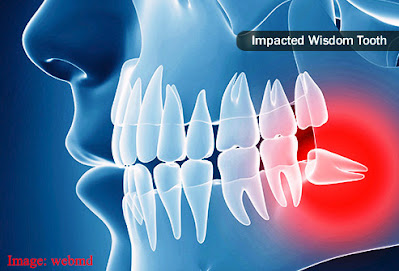
Impacted wisdom teeth are likely to develop cysts (filled with a liquid, gaseous material, or semisolid, much like a blister) around them, harming the tooth and neighboring tissues, including bone. In exceptional circumstances, tumors can develop around these cysts, complicating wisdom teeth removal.
Wisdom teeth can partially appear from underneath the gums. In this site, it is relatively easy for bacteria to enter through the opening around the tooth. If you don't treat, you may experience an infection. The infection will increase wisdom tooth pain, jaw pain, redness, swelling, and general sickness.
Treatment Of Wisdom Teeth

The most popular treatment for wisdom teeth is the removal of the teeth. Wisdom teeth extraction is usually done in an oral surgeon's room under general or local anesthesia. Any complications or options should be discussed before the removal procedure. Sometimes, your surgeon will require cutting the tooth into pieces to rescue as much bone as possible and bypass needlessly cutting bone, and delicate tissues and risking nerves.
Nowadays, dentists recommend wisdom teeth be removed before they become a problem for oral health.
